Momenta's Take: Mind the Skills Gap
Ken Forster

Closing The Industrial Skills Gap –
How Technology Can Help When Experienced Workers Retire
Concerns over AI-driven job destruction have dominated public discourse recently, particularly the potential for societal destabilization as unskilled jobs are replaced by AI. On the other side of the coin, there is currently an acute shortage of workers (unskilled and particularly skilled) in many industries, as a strong labor market makes it increasingly difficult for firms to fill open positions.
As companies become increasingly dependent on advanced technologies, highly skilled workers are increasingly difficult to find and keep. According to a survey from TalentLMS and Workable, 72% of tech employees in the US are considering leaving their jobs in the next year. After losing ~1.4mn jobs at the onset of the pandemic, manufacturing has struggled to fill job vacancies. With massive investments in semiconductor fabs planned for the next decade, McKinsey estimates the US will need about 200,000 to 300,000 more skilled laborers such as electricians, mechanical workers, welders, and pipe fitters.
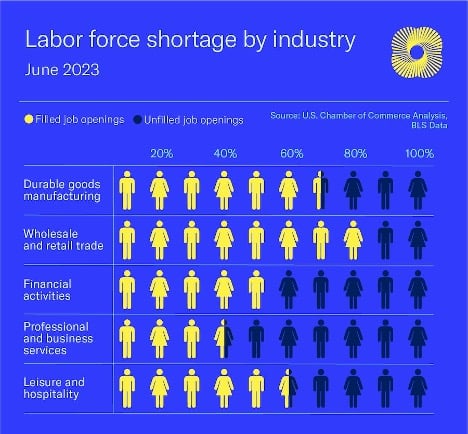
Source: US. Chamber of Commerce Analysis, BLS Data
Retiring Boomers and “The Great Reshuffle”
There are multiple factors at play. Rising expectations among workers post-Pandemic have led to “The Great Resignation” – in 2022, over 50 million quit their jobs – some seeking better work/life balance, better compensation, or company culture.
During the pandemic, 3 million workers retired, and now the entire Baby Boomer generation of 73 million will be 65 or older by 2030. The shortage of Generation X workers is inadequate to fill the gap, and many Millennials lack relevant experience. Additionally, visa challenges make it harder for foreign-born workers, and not every role is suitable for remote workers.
Using HR and Technology to Harness and Cultivate Talent
There are several tactics to address the shortage of skilled labor – by raising wages, investing in training, and through technology and automation.
- Improving Pay and Working Conditions - Businesses face the challenge of attracting, retaining, and nurturing talent to ensure growth and success. To achieve this, it is crucial to offer attractive and competitive pay (a report by the National Bureau of Economic Research indicates that a 10% increase in wages can lead to a 3-5% increase in worker productivity), provide flexible work conditions, and create opportunities for professional development. These factors play a vital role in building a strong and motivated workforce.
- Investing in Targeted Upskilling - Younger generations increasingly gravitate toward university and away from skilled trades, while older workers need to update their skills for digital business. Businesses thus need to invest in relevant training, and in manufacturing, this has become an imperative – a Workforce Institute poll found 63% of manufacturing organizations are currently retraining employees. In comparison, 60% are cross-training their workforce.
- Making Experienced Knowledge More Accessible – Experienced, highly skilled workers who retire take years or even decades of accrued knowledge. Lengthy procedure manuals are difficult for new workers to absorb and often need to be updated. New AI tools can ingest and analyze not just manuals but also emails, records, and external data sources that can be made accessible through ChatBots that workers can query for quick answers or embedded in workflow systems.
- Embracing Advanced Technologies – Manufacturing and industrial firms have long adopted software and hardware automation to help free workers to focus on higher-value tasks. New technologies such as Virtual Reality (for training) and Augmented Reality headsets can equip workers with real-time assistance. IoT sensors and advanced analytics can develop predictive/preventive maintenance systems as a proxy for experienced technicians. 3D Printing technologies can fabricate critical replacement parts for legacy machinery. Collaborative robotics systems can be trained to work alongside human workers, automating tasks while retaining flexibility.
In conclusion, while there's no guaranteed formula for industrial firms to tackle the skilled labor shortage, leveraging technology can be a game-changer. Technology can hold the key to transforming the workforce from onboarding to training, enhancing worker well-being, optimizing workflows, and improving efficiencies and quality management. Embrace the digital wave for a brighter future!

Momenta is the leading Industrial Impact venture capital + growth firm. We accelerate entrepreneurs and leaders devoted to the digitization of energy, manufacturing, smart spaces, and supply chains. Since 2012, our team of deep industry operators have made over 100 investments in entrepreneurs and helped scale over 150 industry leaders via our award-winning executive search and strategic advisory practices.



